The push for more eco-friendly practices has turned the term “biodegradable” into a buzzword across various industries. In many cases, project requirements demand the use of converting to biodegradable materials including lubricants for machines and devices, particularly within applications in environmentally sensitive areas such as forests, beaches, waterways, and other sensitive ecosystems. Other times, companies use the word to show that their brand exercises environmental consciousness to differentiate themselves from the rest of the market.
Bio-based lubricants, such as those in BioBlend’s family of products, have been increasing in popularity since the 1990s, and the demand is now stronger than ever thanks to the many advantages these products provide. But, what is a “biodegradable lubricant,” and why does it matter whether your organization uses one in your projects’ or operations’ resources?
What Is a Biodegradable lubricant?
A biodegradable lubricant is a type of oil or grease that breaks down naturally in the environment through microbial activity, reducing pollution and ecological harm. It is typically made from renewable, plant-based or synthetic materials and provides effective lubrication while being environmentally friendly.
What Is Biodegradability?
Biodegradability is the quality of a substance that is affected by the process of chemical breakdown, degradation or transformation of a material caused by organisms or their enzymes into carbon dioxide and water. Biodegradable matter is generally organic material (compounds with carbon-hydrogen bonds) which serves as a nutrient source for microorganisms.
Substances are subjected to testing using populations of mixed microorganisms including bacteria from natural water or soil. Water, sunlight, and oxygen are needed for optimum aerobic biodegradation to occur. Such tests include:
- ASTM D-5864 Standard Test Method for Determining Aerobic Aquatic Biodegradation of Lubricants
- OECD 301B Modified Sturm Test of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
- EPA 560/6-82-003 Shake Flask Test of the US Environmental Protection Agency.
To pass readily-biodegradable test standards, typically a minimum of 60% degradation of a substance must occur during a 28-day incubation period.
The Difference Between Biodegradable Oil and Grease
Biodegradable lubricants fall into two main categories: oil and grease. They’re both environmentally friendly, but they differ in composition and application. Biodegradable oil is a liquid lubricant designed to reduce friction and wear in machinery, often used in engines, hydraulic systems, and chains. It is formulated to break down naturally in the environment, minimizing pollution.
On the other hand, biodegradable grease is a semi-solid lubricant that consists of biodegradable oil thickened with natural or synthetic thickeners. It provides long-lasting lubrication, resists water washout, and is used in applications requiring more adhesion, such as bearings, gears, and heavy equipment. While both products serve similar functions, the two terms are not interchangeable.
Why Biodegradable Lubricants Are Important
Bio-based lubricants derived from natural plant esters provide superior biodegradability over other lubricant base stocks such as mineral (petroleum) or synthetic stocks. These plant-based esters come from renewable and sustainable crops such as canola, soy, and sunflower oils.
In the event of an oil spill in the field, companies can be liable for any environmental impact. We often hear in the news about the damage inflicted on the environment by oils leaking into landscapes and waterways. These incidents devastate the ecological makeup of the area and lead to huge remediation costs for the companies involved.
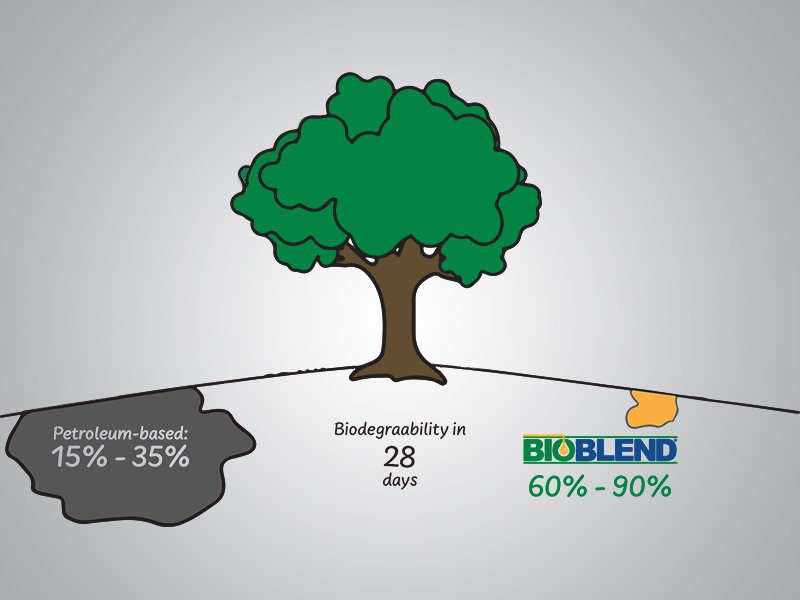
Mineral and petroleum products may have inherent biodegradability, but that means in 28 days only 20-35% of the spill may have biodegraded. However, lubricants with plant-based esters such as BioBlend’s line of sustainable products, can be classified as readily biodegradable (>60%) fluid per the most stringent requirement of OECD 301B.
Moreover, note that biodegradation of hydraulic fluid does NOT occur when the fluid resides within the hydraulic system – it takes soil and/or water microbes, heat/UV radiation and water to catalyze the oil biodegradation process. So, the oil does not start biodegrading until it enters the environment – and does so only if these conditions exist.
Advantages of Using Biodegradable Oil and Grease
The advantages of biodegradable grease and oil, as highlighted by the Society of Tribologists and Lubrication Engineers (STLE), go beyond just environmental benefits and extend to performance, safety, and economic factors. Their advantages include:
- Superior lubricity: Excellent friction reduction, leading to lower wear and longer equipment life
- Higher flash and fire points: Safer to use, reducing the risk of fires in high-temperature applications
- High viscosity index (VI): Maintains stable viscosity across a wide range of temperatures, ensuring consistent performance in varying conditions
Additionally, since they are derived from plant-based oils, their basestock renewability makes them a more sustainable alternative to petroleum-based lubricants, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Don’t Risk It – Go Bio-Based
BioBlend’s renewable and biodegradable lubricants have been formulated to deliver superior performance for many applications that touch the environment such as mining, marine transport, construction, agriculture, forestry, and more. You can be confident that when you use our:
you can count on superior lubrication performance with the least ecological impact.
Take a look at all the industries we serve or contact us to find out how we can assist you in reaching your operational, cost and ESG goals. You may also reach us at +1-888-BIO-BLND (888-246-2563).
Frequently asked questions
What are examples of biodegradable lubricant applications?
Biodegradable lubricants are used in various applications where environmental protection is a priority. In agriculture, they lubricate farm equipment like tractors and harvesters, reducing soil and water contamination. The marine industry relies on biodegradable hydraulic fluids to minimize the environmental impact of leaks in oceans and waterways. Biodegradable oil is also used in forestry equipment, such as chainsaws and logging machinery.
How to dispose of biodegradable oils?
Proper disposal of biodegradable oils is essential to prevent contamination and ensure environmental safety, even though they break down more easily than conventional lubricants. For consumers, small amounts of used biodegradable oil can often be taken to local recycling centers or hazardous waste collection sites, where they are processed safely. Some automotive and hardware stores also accept used oil for recycling. In industrial settings, businesses must follow local regulations for disposal, which may include using specialized waste management companies to collect and recycle or properly treat the oil.
Are synthetic oils biodegradable?
Not all synthetic oils are biodegradable, but some are designed to be. Synthetic oils made from petroleum-based compounds typically do not break down easily in the environment. However, certain synthetic esters and polyalkylene glycols (PAGs) are formulated to be biodegradable, offering the benefits of synthetic performance while minimizing environmental impact.

